
Top predictions from CLIP (ViT-L/14) on ImageNet-D. We synthesize the images by changing their background, texture and material. The groundtruth for the images are plunger, spatula, and ladle in order, together with the background (badminton court), texture (freckled), and material (painted).
Abstract
We establish rigorous benchmarks for visual perception robustness. Synthetic images such as ImageNet-C, ImageNet-9, and Stylized ImageNet provide specific type of evaluation over synthetic corruptions, backgrounds, and textures, yet those robustness benchmarks are restricted in specified variations and have low synthetic quality. In this work, we introduce generative model as a data source for synthesizing hard images that benchmark deep models' robustness. Leveraging diffusion models, we are able to generate images with more diversified backgrounds, textures, and materials than any prior work, where we term this benchmark as ImageNet-D. Experimental results show that ImageNet-D results in a significant accuracy drop to a range of vision models, from the standard ResNet visual classifier to the latest foundation models like CLIP and MiniGPT-4, significantly reducing their accuracy by up to 60\%. Our work suggests that diffusion models can be an effective source to test vision models.
ImageNet-D achieves high image fidelity

Examples from ImageNet-9, Stylized-ImageNet and ImageNet-C and our ImageNet-D. For the second row, we show images from ImageNet-D with different backgrounds, textures and materials orderly. Take the background for example (the two columns on the left), ImageNet-9~\cite{xiao2020noise} generates new images by simply cutting and paste foreground and background from different images, leading to object deformation and dislocation. By contrast, ImageNet-D includes images with diverse backgrounds by diffusion generation, achieving superior visual fidelity.
ImageNet-D samples

The ImageNet-D test set. Each group of images is generated with the same object and nuisance, such as background, texture, and material. For each group of images, the ground truth label is color green, while the predicted categories by CLIP (ViT-L/14) on each image are in black. Leveraging diffusion models for image generation, we can create a test set with diverse combinations of objects and nuisances. For example, the top left corner shows a bench in the swimming pool background. Interestingly, CLIP (ViT-L/14) recognizes the bench in this image as swimming trunks.
Method
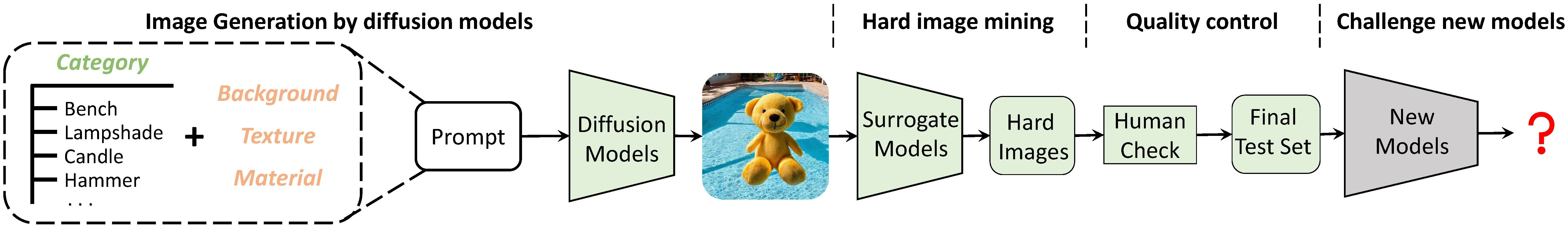
ImageNet-D creation framework. ImageNet-D is created by first combining various object categories and nuisances, including background, texture, and material. To make the test set challenging, we only keep the hard images from the large pool that commonly make multiple surrogate models fail to predict the correct object label. The test set is then refined through human verification to ensure the images are valid, single-class, and high-quality, making ImageNet-D suitable for evaluating the robustness of different neural networks.
Results
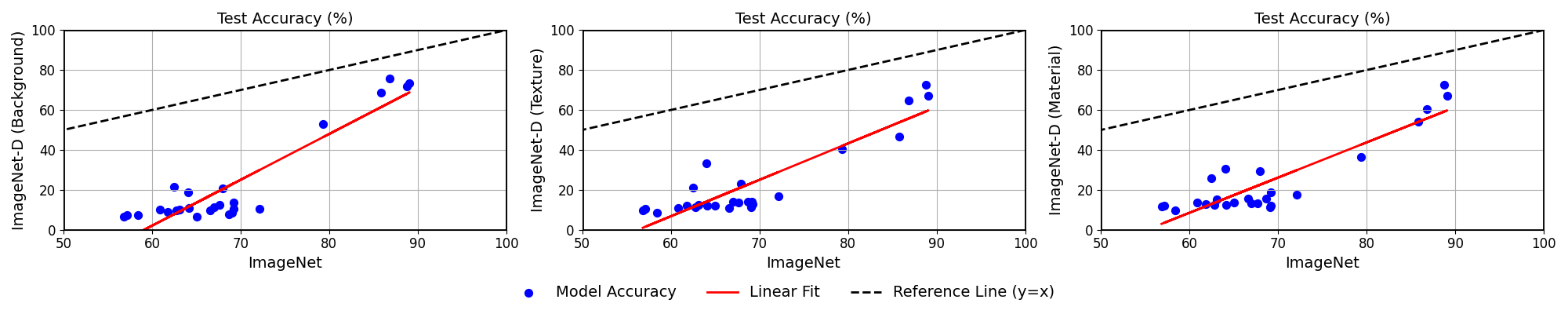
Model accuracy on ImageNet vs. ImageNet-D. Each data point corresponds to one tested model. The plots reveal that there is a significant accuracy drop from ImageNet to our new test set ImageNet-D. As the model's accuracy on ImageNet increases, the accuracy on ImageNet-D is also higher. These results show the effectiveness of ImageNet-D to evaluate the robustness of neural networks.
BibTeX
@article{zhang2024imagenet_d,
author = {Zhang, Chenshuang and Pan, Fei and Kim, Junmo and Kweon, In So and Mao, Chengzhi},
title = {ImageNet-D: Benchmarking Neural Network Robustness on Diffusion Synthetic Object},
journal = {CVPR},
year = {2024},
}